A comprehensive study of technological change
New research using patent data could help inform decision-makers by predicting which technologies are improving the fastest.
Scott Murray | Institute for Data, Systems, and Society
Publication Date :
August 2, 2021
Press Contact :
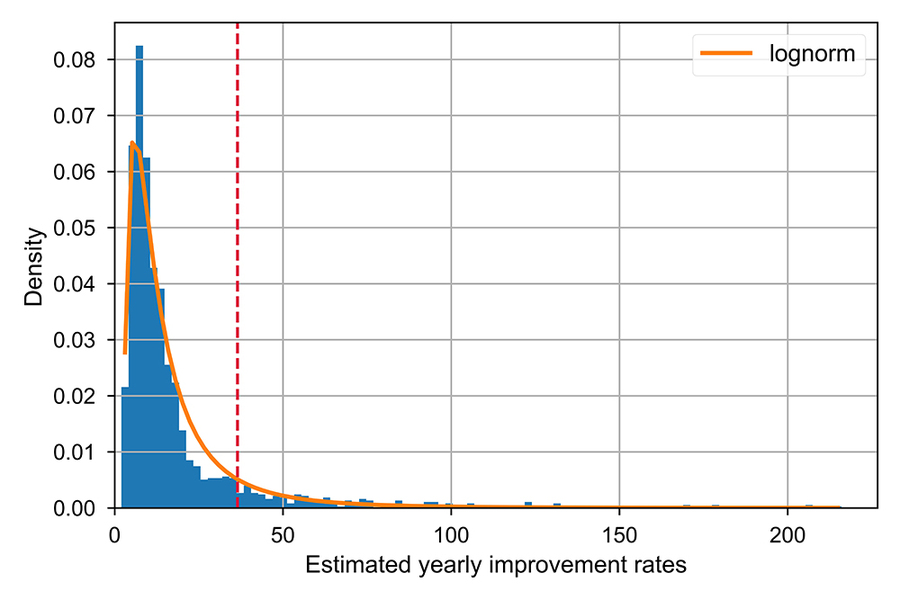 On the y-axis: density, from 0.00 to 0.08. On the X-axis: estimated yearly improvement rates, from 0 to 200. There is a large spike of data going past .08 on the y-axis, in between approximately the 0 and 25 marks on the x-axis. A red vertical dotted line exists at the 36.5 mark." width="900" height="600" />
On the y-axis: density, from 0.00 to 0.08. On the X-axis: estimated yearly improvement rates, from 0 to 200. There is a large spike of data going past .08 on the y-axis, in between approximately the 0 and 25 marks on the x-axis. A red vertical dotted line exists at the 36.5 mark." width="900" height="600" />
Distribution of predicted improvement rates (in percent per year) for all 1,757 technology domains. Domains to the right of dashed red line are improving faster than 36.5 percent per year, the predicted rate for integrated chips according to Moore's law.
Image courtesy of the researchers.
Previous image Next image
The societal impacts of technological change can be seen in many domains, from messenger RNA vaccines and automation to drones and climate change. The pace of that technological change can affect its impact, and how quickly a technology improves in performance can be an indicator of its future importance. For decision-makers like investors, entrepreneurs, and policymakers, predicting which technologies are fast improving (and which are overhyped) can mean the difference between success and failure.
New research from MIT aims to assist in the prediction of technology performance improvement using U.S. patents as a dataset. The study describes 97 percent of the U.S. patent system as a set of 1,757 discrete technology domains, and quantitatively assesses each domain for its improvement potential.
“The rate of improvement can only be empirically estimated when substantial performance measurements are made over long time periods,” says Anuraag Singh SM ’20, lead author of the paper. “In some large technological fields, including software and clinical medicine, such measures have rarely, if ever, been made.”
A previous MIT study provided empirical measures for 30 technological domains, but the patent sets identified for those technologies cover less than 15 percent of the patents in the U.S. patent system. The major purpose of this new study is to provide predictions of the performance improvement rates for the thousands of domains not accessed by empirical measurement. To accomplish this, the researchers developed a method using a new probability-based algorithm, machine learning, natural language processing, and patent network analytics.
Overlap and centrality
A technology domain, as the researchers define it, consists of sets of artifacts fulfilling a specific function using a specific branch of scientific knowledge. To find the patents that best represent a domain, the team built on previous research conducted by co-author Chris Magee, a professor of the practice of engineering systems within the Institute for Data, Systems, and Society (IDSS). Magee and his colleagues found that by looking for patent overlap between the U.S. and international patent-classification systems, they could quickly identify patents that best represent a technology. The researchers ultimately created a correspondence of all patents within the U.S. patent system to a set of 1,757 technology domains.
To estimate performance improvement, Singh employed a method refined by co-authors Magee and Giorgio Triulzi, a researcher with the Sociotechnical Systems Research Center (SSRC) within IDSS and an assistant professor at Universidad de los Andes in Colombia. Their method is based on the average “centrality” of patents in the patent citation network. Centrality refers to multiple criteria for determining the ranking or importance of nodes within a network.
“Our method provides predictions of performance improvement rates for nearly all definable technologies for the first time,” says Singh.
Those rates vary — from a low of 2 percent per year for the “Mechanical skin treatment — Hair removal and wrinkles” domain to a high of 216 percent per year for the “Dynamic information exchange and support systems integrating multiple channels” domain. The researchers found that most technologies improve slowly; more than 80 percent of technologies improve at less than 25 percent per year. Notably, the number of patents in a technological area was not a strong indicator of a higher improvement rate.
“Fast-improving domains are concentrated in a few technological areas,” says Magee. “The domains that show improvement rates greater than the predicted rate for integrated chips — 42 percent, from Moore’s law — are predominantly based upon software and algorithms.”
TechNext Inc.
The researchers built an online interactive system where domains corresponding to technology-related keywords can be found along with their improvement rates. Users can input a keyword describing a technology and the system returns a prediction of improvement for the technological domain, an automated measure of the quality of the match between the keyword and the domain, and patent sets so that the reader can judge the semantic quality of the match.
Moving forward, the researchers have founded a new MIT spinoff called TechNext Inc. to further refine this technology and use it to help leaders make better decisions, from budgets to investment priorities to technology policy. Like any inventors, Magee and his colleagues want to protect their intellectual property rights. To that end, they have applied for a patent for their novel system and its unique methodology.
“Technologies that improve faster win the market,” says Singh. “Our search system enables technology managers, investors, policymakers, and entrepreneurs to quickly look up predictions of improvement rates for specific technologies.”
Adds Magee: “Our goal is to bring greater accuracy, precision, and repeatability to the as-yet fuzzy art of technology forecasting.”

 On the y-axis: density, from 0.00 to 0.08. On the X-axis: estimated yearly improvement rates, from 0 to 200. There is a large spike of data going past .08 on the y-axis, in between approximately the 0 and 25 marks on the x-axis. A red vertical dotted line exists at the 36.5 mark." width="900" height="600" />
On the y-axis: density, from 0.00 to 0.08. On the X-axis: estimated yearly improvement rates, from 0 to 200. There is a large spike of data going past .08 on the y-axis, in between approximately the 0 and 25 marks on the x-axis. A red vertical dotted line exists at the 36.5 mark." width="900" height="600" />